Our mission
Brussels Centre of Competition Policy is a centre of excellence for interdisciplinary research on competition and industrial policy.
Within this context, BCCP:
- brings together all VUB expertise in this area, more particularly from the Faculty of Social Sciences and Solvay Business School, the Faculty of Law, and the Brussels School of Governance.
- fosters interdisciplinary research on competition and industrial policy and this at the theoretical, methodological and empirical level.
- focuses on high quality publications and scientific (inter)national collaborations.
- provides advisory services for public and private partners and organises interdisciplinary conferences and trainings.
What is Competition Policy?
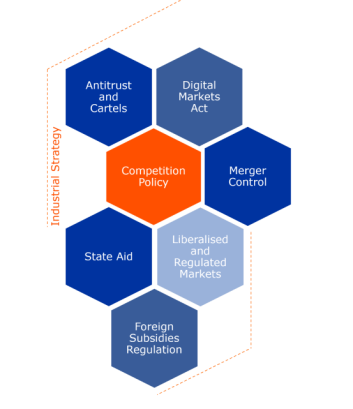
Competition policy exists to preserve the well-being or optimal functioning of free markets. Its core assumption is that anti-competitive behaviour must be prevented, discouraged, or sanctioned ex post. Sound competition is important for keeping prices of goods and services low, ensure a wide range of choice, high quality and a healthy level of innovation. There are four main pillars within the field of competition policy, i.e. state aid, antitrust, merger control and liberalisation/privatisation of markets.
Competition policy is a domain that is of relevance to all sectors (including public) in society, that touches upon a vast amount of subnational, national, European, and international policy domains, making it significant for researchers, practitioners and policymakers from diverse disciplines.
Many competition cases also touch upon broader public interest considerations such as environmental protection and privacy, triggering the debate on how these topics could or should be integrated within competition policy.
At the same time, strict EU competition policy is not without critique from industry as it has been accused of hampering the growth and consolidation of EU players to compete in the global market, especially considering the dramatic geopolitical changes of the last years. Consequently, competition rules are placed again within the wider frame of industrial policy, where diverse government interventions are considered to create a favourable industrial structure to promote competitiveness and productivity-based growth.






